webapp.programme¶
Widget definition module: Defines UI elements used for entering heating run parameters, such as target temperature, heat rate and hold time.
Use the following code to import and display the widgets defined in this module:
- example:
>>> from webapp import programme
>>> display(programme.app)
Widget layout¶
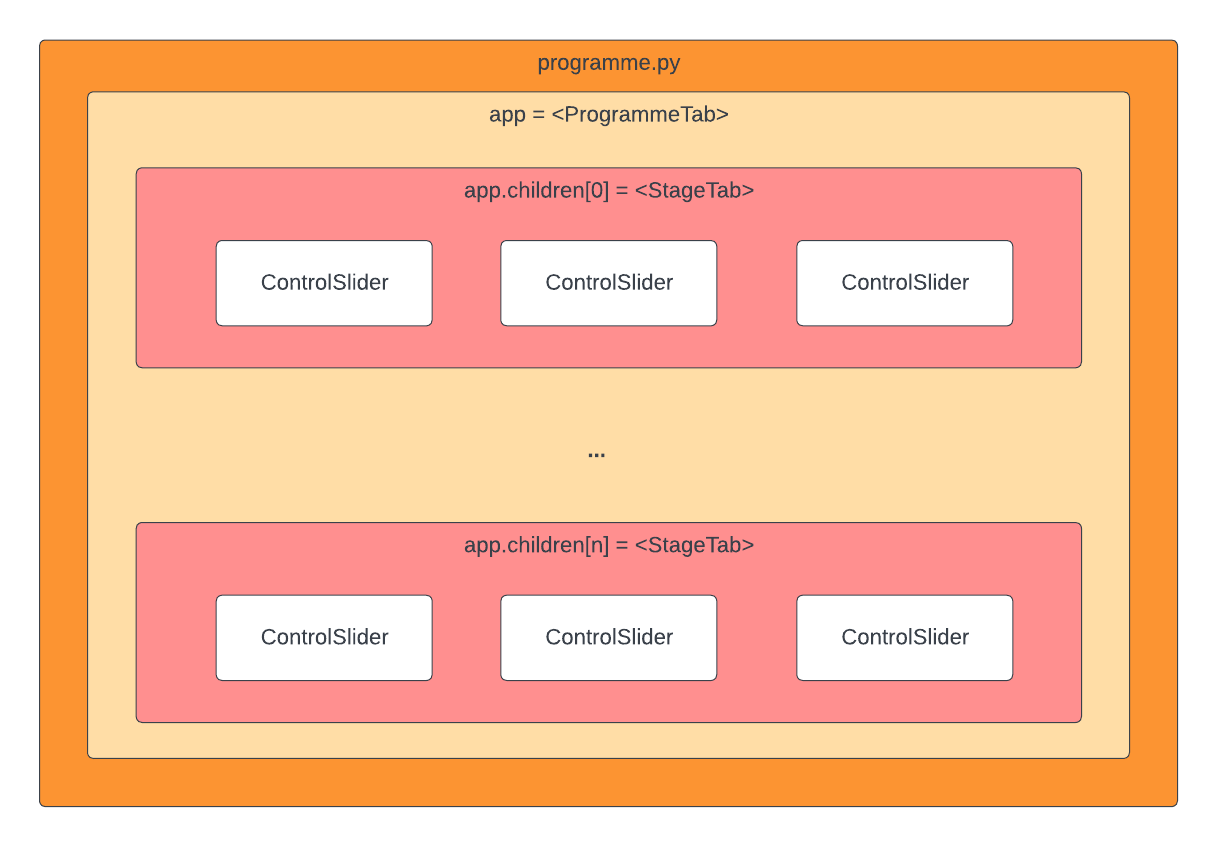
Widget objects¶
- webapp.programme.app <webapp.programme.ProgrammeTab>¶
Module top-level container widget - holds all the widgets defined in the
webapp.programmemodule, which make up the Programme tab in the dashboard app.Allows the Programme tab to be imported into the dashboard app using the code below:
- Example:
>>> from webapp import programme >>> programme.app
Helper classes¶
- class webapp.programme.ProgrammeTab(**kwargs: Any)¶
Customised subclass of
ipywidgets.widgets.Tabwidget, styled to provide a tabbed interface, where each tab represents a sequential temperature stage in the heating programme.A
ProgrammeTabobject therefore contains a number ofStageTabobjects, which themselves contain slider widgets for setting the target temperature, heat rate and hold time for each temperature stage.In order to facilitate arbitrary numbers of temperature stages, the
new_tab_callback()andadd_tab()methods provide a way of adding additionalStageTabinstances to an instance ofProgrammeTab, as that functionality is not provided by theipywidgets.widgets.Tabclass at the time of writing.- add_tab()¶
Add a new
StageTabto theProgrammeTabwidget and, correspondingly, a new stage towebapp.shared.appState.programme
- new_tab_callback(change)¶
Callback function used to check whether a new tab should be added.
Works in conjunction with the ipywidgets.widgets.Widget.observe() method, (see
ProgrammeTab.__init__()), which will call this method whenever the widget’s selected tab changes.- Parameters:
change (
dict) – Dictionary of the form{'name': 'selected_index', 'old': x, 'new': y, 'owner': ProgrammeTab}, wherexis the index of the previously selected tab, andyis the index of the newly selected tab.
- reset()¶
Reset to idle settings. Called when the ‘Reset’ button is pressed, as well as after a heating programme has finished.
- class webapp.programme.StageTab(**kwargs: Any)¶
Customised subclass of
ipywidgets.widgets.Accordionwidget, styled to provide a group of sliders for setting the three parameters in a temperature stage.- Parameters:
stage (
ResponsiveDict{str: int, str: int, str: int}) –ResponsiveDictof the formResponsiveDict({'TEMP': X, 'HEAT': Y, 'HOLD': Z}), where the dictionary values specify the target temperature, heating rate and hold time for the stage, respectively.
- class webapp.programme.ControlSlider(**kwargs: Any)¶
Customised extension of
ipywidgets.widgets.IntSliderwidget, styled to provide a slider that controls a single parameter in a temperature stage.- Parameters:
stage (
dict{str: int, str: int, str: int}) – Adict-type object, of the following form,{'TEMP': X, 'HEAT': Y, 'HOLD': Z},target (
str) – The key for the item instagethat the slider will control.
Code listing¶
"""
Widget definition module: Defines UI elements used for entering heating
run parameters, such as target temperature, heat rate and hold time.
Use the following code to import and display the widgets defined in this module:
:example:
>>> from webapp import programme
>>> display(programme.app)
"""
# Import the widgets we need to use
from ipywidgets.widgets import IntSlider, Tab, Accordion
from ipywidgets.widgets import Layout
from IPython.core.display import display, HTML # IPython Notebook functions
# Import global settings, to be able to change the config
from webapp.shared import appState
from webapp.utils import ResponsiveDict
class ProgrammeTab(Tab):
"""
Customised subclass of :external:class:`ipywidgets.widgets.Tab` widget, styled to
provide a tabbed interface, where each tab represents a sequential
temperature stage in the heating programme.
A :class:`ProgrammeTab` object therefore contains a number of :class:`StageTab`
objects, which themselves contain slider widgets for setting the target
temperature, heat rate and hold time for each temperature stage.
In order to facilitate arbitrary numbers of temperature stages, the
:meth:`new_tab_callback` and :meth:`add_tab` methods provide a way of adding
additional :class:`StageTab` instances to an instance of :class:`ProgrammeTab`,
as that functionality is not provided by the :external:class:`ipywidgets.widgets.Tab`
class at the time of writing.
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
global appState
super().__init__(
children =
[
# One stage tab for each stage in the programme, plus one
# more for the '+' tab
*[StageTab(stage) for stage in appState.programme.stages],
StageTab()
]
)
# Label the tabs with their stage numbers
for i, _ in enumerate(appState.programme.stages):
self.set_title(i, 'Stage {}:'.format(i+1))
# Last tab is the '+' tab
self.set_title(len(appState.programme.stages), '+')
# Default to the first tab (because defaulting to the '+' tab
# is a VERY bad idea)
self.selected_index = 0
# Add an observer to the selected_index attribute, so that whenever
# the selected tab changes, the ``new_tab_callback`` method is called
# in response.
self.observe(self.new_tab_callback, names='selected_index')
def new_tab_callback(self, change):
"""
Callback function used to check whether a new tab should be added.
Works in conjunction with the `ipywidgets.widgets.Widget.observe() <https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/7.6.2/examples/Widget%20Events.html?highlight=observe#Traitlet-events>`_
method, (see :meth:`ProgrammeTab.__init__`), which will
call this method whenever the widget's selected tab changes.
:param change: Dictionary of the form ``{'name': 'selected_index',
'old': x, 'new': y, 'owner': ProgrammeTab}``, where ``x`` is
the index of the previously selected tab, and ``y`` is the
index of the newly selected tab.
:type change: ``dict``
"""
# What is the index of the newly selected tab?
new_tab_index = change['new']
# Was the '+' tab selected?
if new_tab_index == len(self.children)-1:
# Yes, therefore we need to add a new tab
self.add_tab()
def add_tab(self):
"""
Add a new :class:`StageTab` to the
:class:`ProgrammeTab` widget and, correspondingly, a new
stage to :attr:`webapp.shared.appState.programme`
"""
global appState
# Are we adding the first stage?
if len(appState.programme.stages) > 0:
# No, therefore add a new stage to the end of the programme
# with initial values equal to the last stage
new_stage = appState.programme.stages[-1].copy()
appState.programme.add_stage(new_stage)
else:
# Yes, therefore add a new stage with the idle settings of room
# temperature and no heating
appState.programme.add_stage({'TEMP:': 23, 'HEAT': 0, 'HOLD': 0})
# Define the new tab layout
tabs = [StageTab(stage) for stage in appState.programme.stages]
# Assign the new tab layout to the ``ProgrammeTab`` widget
self.children = [*tabs, StageTab()]
# Relabel the tabs with their stage numbers
for i, stage in enumerate(appState.programme.stages):
self.set_title(i, 'Stage {}'.format(i+1))
self.set_title(len(appState.programme.stages), '+')
# Set the selected tab to the newest one
self.selected_index = len(self.children) - 2
def reset(self):
"""
Reset to idle settings. Called when the 'Reset' button is pressed, as well as
after a heating programme has finished.
"""
#breakpoint()
self.__init__()
#self.children = [StageTab(stage) for stage in appState.programme.stages]
class StageTab(Accordion):
"""
Customised subclass of ``ipywidgets.widgets.Accordion`` widget, styled to
provide a group of sliders for setting the three parameters in a
temperature stage.
:param stage: ``ResponsiveDict`` of the form
``ResponsiveDict({'TEMP': X, 'HEAT': Y, 'HOLD': Z})``, where the
dictionary values specify the *target temperature*, *heating rate*
and *hold time* for the stage, respectively.
:type stage: ``ResponsiveDict{str: int, str: int, str: int}``
"""
def __init__(self, stage=
ResponsiveDict(
{
'TEMP': 23,
'HEAT': 0,
'HOLD': 0
}
),
**kwargs
):
self.stage = stage
super().__init__(
children=
[
ControlSlider(self.stage, 'TEMP'),
ControlSlider(self.stage, 'HEAT'),
ControlSlider(self.stage, 'HOLD')
],
layout=Layout(width='100%'),
**kwargs
)
self.set_title(0, 'Target Temperature')
self.children[0].value=self.stage['TEMP']
self.children[0].min=0
self.children[0].max=200
self.set_title(1, 'Heating rate')
self.children[1].value=abs(self.stage['HEAT'])
self.children[1].min=0.001
self.children[1].max=30
self.set_title(2, 'Hold Time')
self.children[2].value=self.stage['HOLD']
self.children[2].min=0
self.children[2].max=180
class ControlSlider(IntSlider):
"""
Customised extension of ``ipywidgets.widgets.IntSlider`` widget, styled to
provide a slider that controls a single parameter in a temperature stage.
:param stage: A ``dict``-type object, of the following form,
``{'TEMP': X, 'HEAT': Y, 'HOLD': Z}``,
:type stage: ``dict{str: int, str: int, str: int}``
:param target: The key for the item in ``stage`` that the slider will control.
:type target: ``str``
"""
def __init__(self, stage, target, **kwargs):
super().__init__(
value=22,
min=0,
max=200,
step=1,
disabled=False,
continuous_update=False,
orientation='horizontal',
readout=True,
readout_format='d',
layout=Layout(width='100%'),
**kwargs
)
self.stage = stage
self.target = target
self.observe(self.handle_slider_change, names='value')
def handle_slider_change(self, change):
self.stage[self.target] = change['new']
app = ProgrammeTab(
layout=Layout(margin='0 0 0 0',maxwidth='81.25%',maxheight='83.33%',
padding='0 0 0 0')
)
"""
Module top-level container widget - holds all the widgets defined in the
:mod:`webapp.programme` module, which make up the Programme tab in the
dashboard app.
Allows the Programme tab to be imported into the dashboard app using the
code below:
:example:
>>> from webapp import programme
>>> programme.app
"""