Interface reference¶
Overview¶
The previous sections covered the implementation of the system-level features
in the web app program [:doc:_ref_ui_overview], in addition to the
electronics integration and control handled by the microcontroller program
[:doc:_ref_micro_overview].
In order for these two programs to communicate with each other, an additional python program
Whilst the previous sections covered the implementation of the high-level,
user-facing control of the system [:doc:_ref_ui_overview], as well as
the lower-level electronic control routines handled by the
[:doc:_ref_micro_overview], the means by which both programs communicate
with each other was not discussed in a lot of detail.
As previously mentioned in the the basic section, the dashboard-style user interface for the system is built using a widget based approach, that relies on the Jupyter interactive computing platform.
This approach was chosen for the following reasons:
As a Python-based project, the Jupyter platform is a natural fit, providing a popular, well-documented Python environment that is capable of producing rich interactive, web-based visualisations, using python libraries and code which should be familiar to undergraduates who have a grounding in Python programming.
Modern web browsers provide an ideal deployment platform for graphical applications, offering compatibility across a wide range of devices, operating systems and user interfaces (mouse, or touchscreen).
app¶
Top-level widget definition module: Handles setup and arrangement of widgets defined in submodules, as well as connection of dashboard app to microcontroller.
Widget layout¶
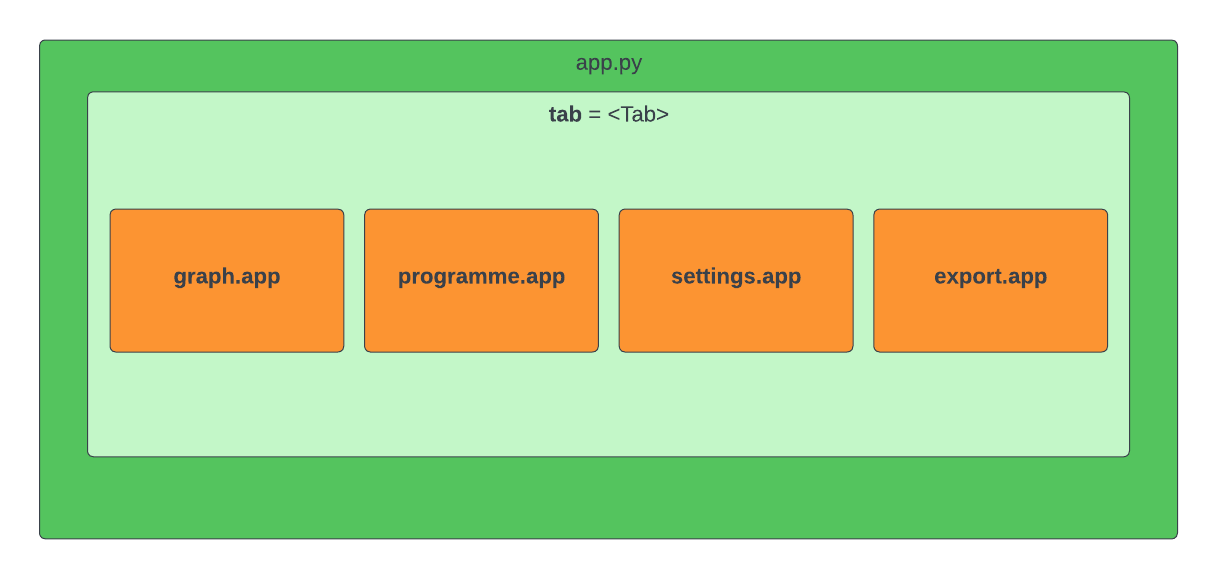
Widget objects¶
- app.tab <ipywidgets.widgets.Tab>¶
Displays children each on a separate accordion tab.
Helper functions¶
- async app.work(reader, writer)¶
This is the routine that handles the datastream from the microcontroller, reading in uploaded sensor data and storing it in the global variables, as well as monitoring the microcontroller configuration, to ensure it is in sync with the user interface software.
- async app.main()¶